MNE Python
MNE Python is an excellent, open-source choice for EEG (and MEG) data visualization and analysis.
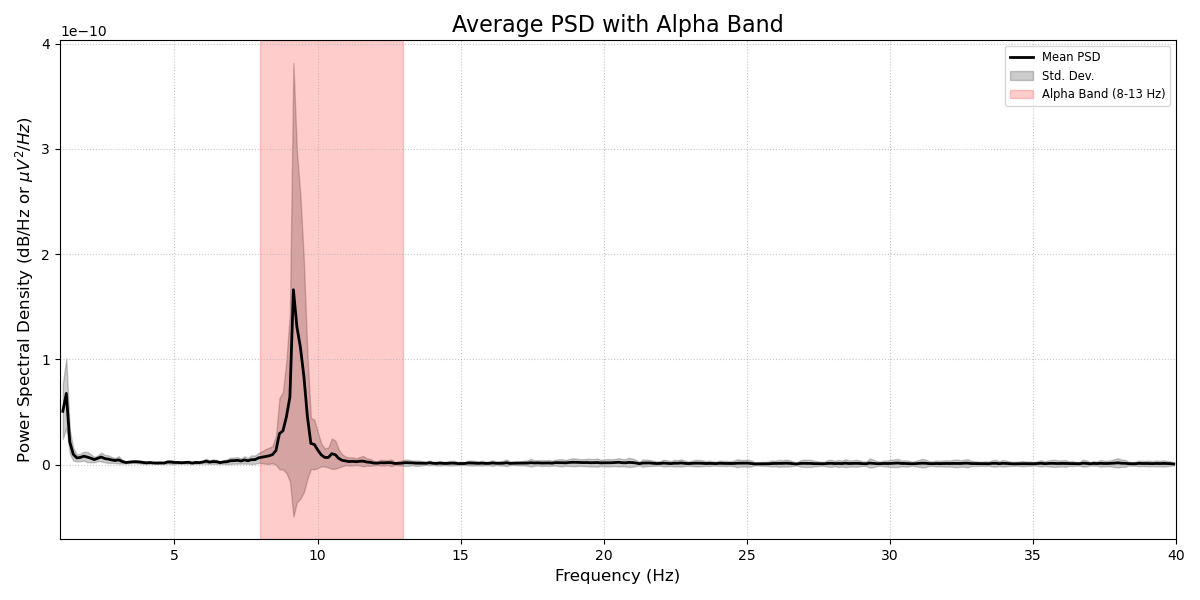
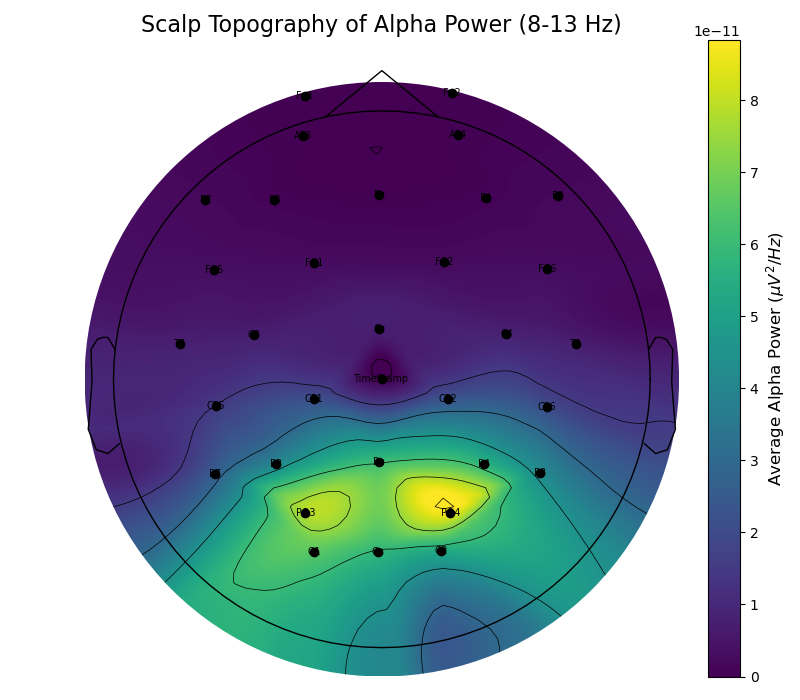
Loading Mentalab data into MNE
CSV and BDF files
The below script can be used to create an mne raw data object from a .csv or .bdf file recorded with Explore Desktop. For CSV, the mne object is created from a simple pandas data_frame. Reading bdf files uses the bdf file loader provided by mne.
XDF files
The function can also be used to read in an xdf file recorded with LabRecorder (relying on the pyxdf library). Loading xdf files selects the first stream in the file by default. Change it by adjusting the stream_num variable. Make sure to select the correct ExG stream, as there may be several ExG, ORN, and Marker streams in one xdf file.
BIN files
To load a Mentalab binary (*.BIN) taken from the amplifiers flash memory, convert it to csv or bdf using Explore Dekstop (File > Convert BIN) first and then continue with the below function.
In all cases, the function will automatically determine the number of channels, channel names, and sampling rate for you.
Do note that Mentalab ExG data is always recorded raw, meaning that after creating the mne raw object, you have free choice of processing in terms of filtering, artefact rejection, and so on.
###########################
### Mentalab MNE Loader ###
###########################
# The below script can be used to create an mne raw data object
# from a csv or bdf file recorded with Explore Desktop,
# or an xdf file recorded with LabRecorder.
#
# Loading xdf files selects the first stream in the file by default.
# Change it by adjusting the stream_num variable.
# Make sure to select the correct ExG stream, as there may be several ExG,
# ORN, and Marker streams in one xdf file.
#
# To load a Mentalab binary (*.BIN) taken from the amplifiers flash memory,
# convert it to csv or bdf using Explore Dekstop (File > Convert BIN) first
# and then continue with the below function.
import pandas as pd
import pyxdf
import mne
def mne_load_mentalab(file_name):
# CSV
if file_name.split('.')[1] == "csv":
print(f"Creating mne raw object from csv.")
file_name_root = file_name.split('.')[0][:-4]
sampling_freq = pd.read_csv(file_name_root + '_Meta.csv', delimiter=',')['sr'][0]
data_frame = pd.read_csv(file_name, delimiter=',')
data_frame = data_frame.drop('TimeStamp', axis = 1)
n_channels = len(data_frame.columns)
ch_types = ["eeg"] * n_channels
ch_names = list(data_frame.columns)
info = mne.create_info(ch_names=ch_names,
sfreq=sampling_freq,
ch_types=ch_types)
# convert from muVolt to Volt because MNE expects data in Volt units
data_frame = data_frame.div(1e6)
data_frame = data_frame.transpose()
raw_data = mne.io.RawArray(data_frame, info)
return raw_data
# BDF
elif file_name.split('.')[1] == 'bdf':
print(f"Creating mne raw object from bdf.")
raw_data = mne.io.read_raw_bdf(file_name)
return raw_data
# XDF
elif file_name.split('.')[1] == 'xdf':
streams, header = pyxdf.load_xdf(file_name)
# THIS SELECTS THE FIRST STREAM
# CHANGE INDEX TO SWITCH STREAM
stream_num = 1
print(f"Creating mne raw object from xdf. Selected stream: {stream_num}.")
ch_names = []
for x in streams[stream_num]['info']['desc'][0]['channels'][0]['channel']:
ch_names.append(x['name'][0])
data = streams[stream_num]["time_series"].T
n_channels = data.shape[0]
sampling_freq = float(streams[stream_num]["info"]["nominal_srate"][0])
# convert from muVolt to Volt because MNE expects data in Volt units
data *= 1e-6 # uV -> V
info = mne.create_info(ch_names, sampling_freq, ["eeg"] * n_channels)
raw_data = mne.io.RawArray(data, info)
return raw_data
# Usage example calls
raw_data = mne_load_mentalab("data/8channel_ExG.csv")
raw_data = mne_load_mentalab("data/16channel_ExG.bdf")
raw_data = mne_load_mentalab("data/32channel_ExG.xdf")
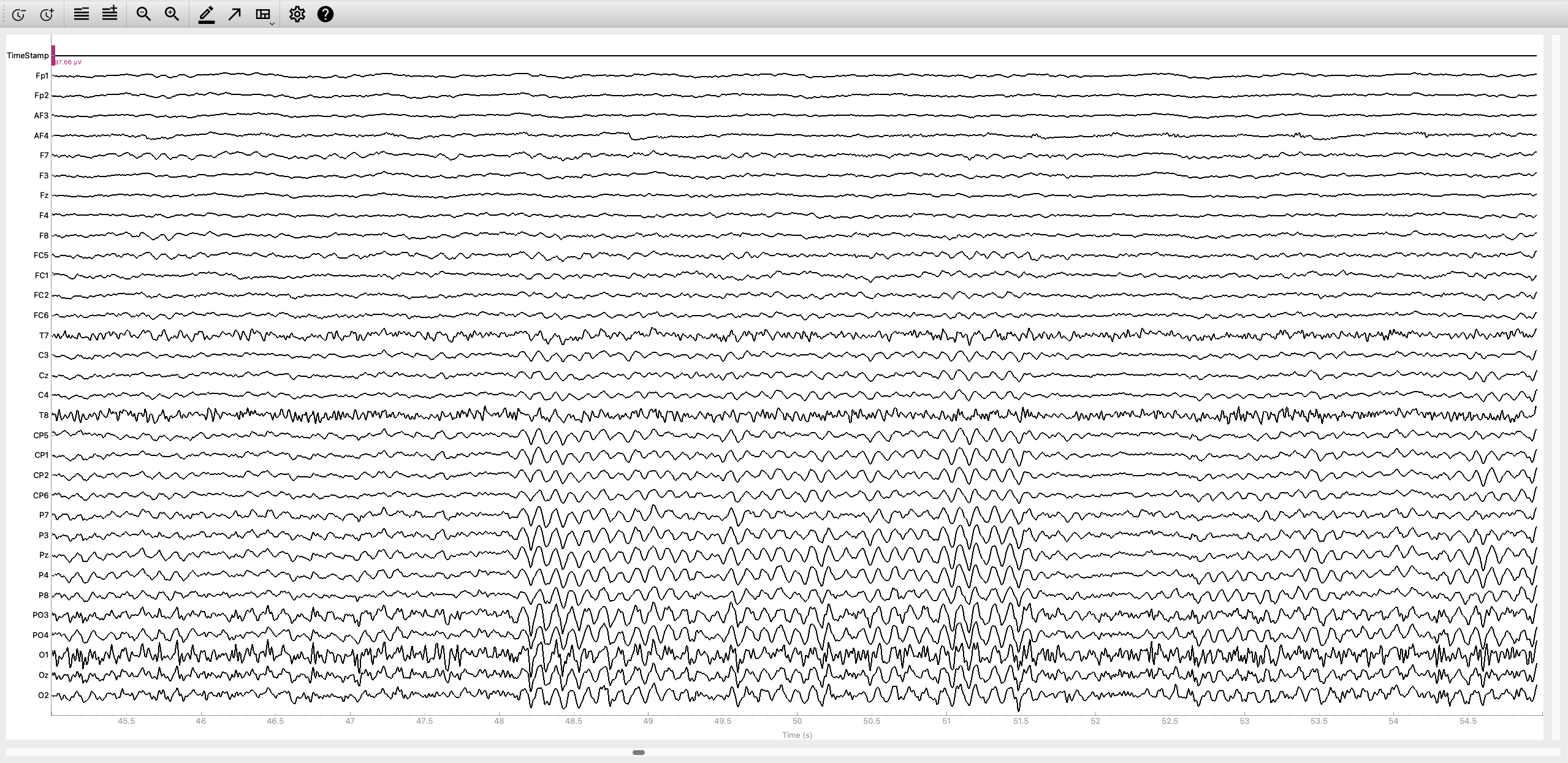
Having loaded your data, you can now filter your data to taste and use raw_data.plot() to inspect your recording.
For more information or support, do not hesitate to get in contact at: support@mentalab.com